National Observer: Canada joins other countries examining dirty marine fuel ban
The use of these types of fuels “will lead to a massive increase in black carbon emissions” that will “both accelerate the melting of Arctic sea ice and have a major impact on Earth’s climate,” argued the alliance’s lead advisor Sian Prior.
Arctic Frontiers Event: “Moving towards a ban on heavy fuel oil (HFO) in the Arctic”

Please join the Clean Arctic Alliance and Bellona Foundation for an event welcoming new signatories to the Arctic Commitment, and to hear from operators, government and NGOs on what their policy, commitment and solutions are for a more sustainable Arctic.
Oil companies must explain how their new “Super Pollutant” shipping fuels ever came to market

Responding to the discovery that some of the new blended low sulphur shipping fuels developed and marketed by oil companies to comply with IMO 2020 air pollution standards will actually lead to a surge in the emissions of a Super Pollutant known as Black Carbon, the Clean Arctic Alliance is calling for the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to support an immediate switch to distillate fuels for ships in the Arctic and develop a global rule prohibiting fuels with high Black Carbon emissions
High North News: IMO Mandate For Low Sulphur Fuel Results in High Black Carbon Emissions Endangering Arctic
Scientists and environmentalists are sounding the alarm as this new type of fuel can unexpectedly result in high levels of black carbon – a pollutant especially harmful to the Arctic environment.
MEPC 75/5/4: The need for an urgent switch to distillates for ships operating in the Arctic

This document discusses the implications for the Arctic of a recent study indicating that blended low sulphur residual fuels that have been developed to meet the IMO 2020 sulphur limit requirement will result in a significant increase in Black Carbon emissions, and calls on IMO to mandate an urgent switch to distillates for ships operating in the Arctic to avoid a sharp rise in emissions of short-lived climate forcers in this vulnerable area
Infographic: The Use of Heavy Fuel Oil in Arctic Shipping
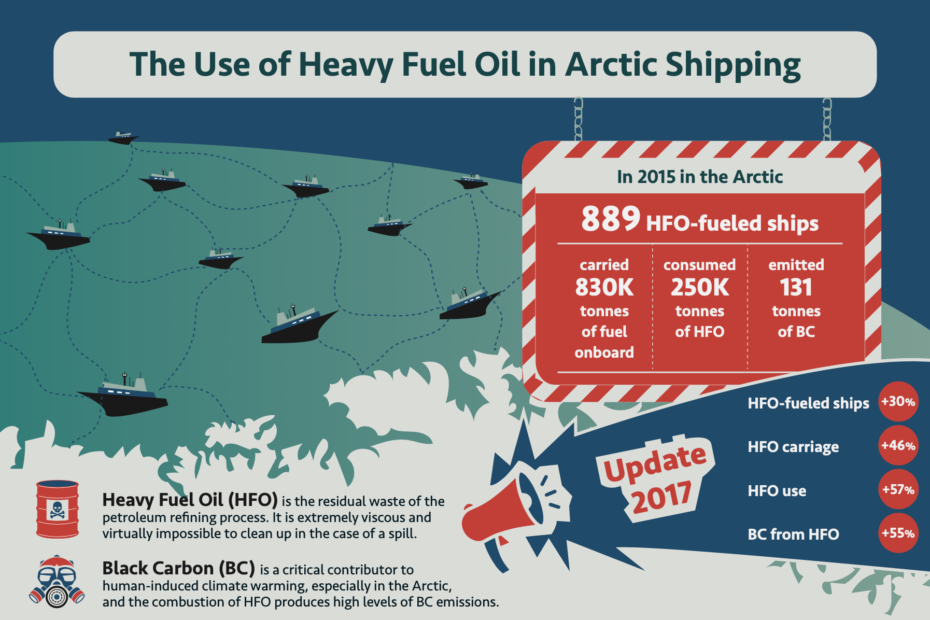
This infographic details how many ship operating in the Arctic use heavy fuel oil (HFO) – the residual waste of the petroleum refining process. It is extremely viscous and virtually impossible to clean up in the case of a spill. It also looks at Black Carbon, a critical contributor to human-induced climate warming, especially in the Arctic. The combustion of heavy fuel oil produces high levels of Black Carbon.
PPR7 Submission: The need for urgent action to stop the use of blended low sulphur residual fuels leading to increases in ship-source Black Carbon globally

This document responds to a recent study showing that new blended low sulphur residual fuels designed to meet the IMO 2020 mandated 0.50% global sulphur limit will result in very significant increases in ships’ Black Carbon emissions, reflects on the implications of this for shipping’s contribution to the climate crisis and calls on IMO to regulate to stop their use
PPR7 Submission: The need for an urgent switch to distillates for ships operating in the Arctic

This document discusses the implications for the Arctic of a recent study indicating that blended low sulphur residual fuels that have been developed to meet the IMO 2020 requirement will result in a significant increases in Black Carbon emissions, and calls on the IMO to mandate an urgent switch to distillates for ships operating in the Arctic to avoid a sharp rise in emissions of short-lived climate forcers in this vulnerable area
Lloyds List: The Erika Heavy Fuel Oil Spill – 20 Years On

The anniversary of the Erika HFO spill serves as a stark reminder of the need for urgent action to protect the Arctic from HFO spills, while the recent evidence from fuel oil spills demonstrates that only a few hundred tonnes of HFO could easily lead to an ecological disaster in the Arctic
The Erika Heavy Fuel Oil Spill – 20 Years On

‘The anniversary of the Erika HFO spill serves as a stark reminder of the need for urgent action to protect the Arctic from HFO spills, while the recent evidence from fuel oil spills demonstrates that only a few hundred tonnes of HFO could easily lead to an ecological disaster in the Arctic,’ argues Dr Sian Prior

